Publications
Spacer Fidelity Assessments of Guide RNA by Top-Down Mass Spectrometry
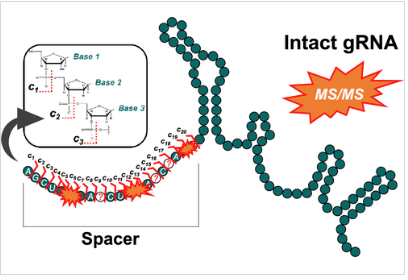
ABSTRACT: The advancement of CRISPR-based gene editing tools into biotherapeutics offers the potential for cures to genetic disorders and for new treatment paradigms for even common diseases. Arguably, the most important component of a CRISPR-based medicine is the guide RNA, which is generally large (>100-mer) synthetic RNA composed of a “tracr” and “spacer” region, the latter of which dictates the on-target editing site as well as potential undesired off-target edits.
Aiming to advance contemporary capabilities for gRNA characterization to ensure the spacer region is of high fidelity, top-down mass spectrometry was herein implemented to provide direct and quantitative assessments of highly modified gRNA. In addition to sequencing the spacer region and pinpointing modifications, top-down mass spectra were utilized to quantify single-base spacer substitution impurities down to U and U > C substitutions, and created a de novo sequencing strategy to facilitate the identification and quantification of gRNA impurities with highly dissimilar spacer regions.
Explore the detailed study on Spacer Fidelity Assessments of Guide RNA by Top-Down Mass Spectrometry, featured in ACS Central Science.

A Sampling of MassMatrix's Chief Scientific Officer's (Mike Freitas, Ph.D.) Research
Xu H, Zhang L, Freitas MA. Identification and characterization of disulfide bonds in proteins and peptides from tandem MS data by use of the MassMatrix MS/MS search engine. J Proteome Res. 2008 Jan;7(1):138-44. doi: 10.1021/pr070363z. Epub 2007 Dec 12. PMID: 18072732; PMCID: PMC2749473.
